BRICS Membership : What Is It, Who Wants In, and Why? 2025
BRICS Membership
BRICS—a coalition of five major emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—commands attention globally. Representing over 40% of the world’s population and a significant chunk of its economic power, BRICS is viewed as a counterbalance to Western economic influence, particularly that of the U.S. Over the years, this coalition has drawn interest from other nations keen to join and align with its goals. This post explores the origins, motivations, and potential future of BRICS, providing a deeper look at why other countries are eager to join and how this could reshape global dynamics.

What Is BRICS?
Origins and Purpose of BRICS
The concept of BRICS originated in 2001 when a Goldman Sachs economist coined the acronym “BRIC” to denote the growth potential of four emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, and China. Together, these nations were projected to play a prominent role in the global economy. By 2009, the BRIC coalition was formalized, with Russia initiating its creation. South Africa joined in 2010, expanding the group to BRICS.
Unlike formal multilateral organizations such as the United Nations (UN) or World Bank, BRICS operates as an informal alliance. Its structure does not involve a centralized headquarters or a stringent membership framework. Instead, each member country rotates as chair of the group annually, directing its agenda and organizing summits. Decisions are made by consensus, allowing members to preserve their autonomy while working collectively toward shared goals.
Objectives of BRICS
The group’s focus extends beyond geopolitical strategy. Key goals include economic cooperation, increasing multilateral trade, and fostering development among member nations. These objectives have made BRICS particularly attractive to other emerging economies seeking an alternative to Western-dominated financial systems and organizations.
Who Wants to Join BRICS?
As BRICS seeks to expand its influence, numerous countries have expressed interest in joining. In 2023, South Africa, the group’s current chair, reported that over 40 countries showed interest in BRICS membership. Here are some notable contenders:
- Iran:
Iran has openly voiced its desire to join BRICS, hoping to accelerate the membership process. Its strategic location and vast oil resources make it a potentially valuable addition. - Saudi Arabia:
As a leading oil producer, Saudi Arabia has garnered support from Russia and Brazil for BRICS membership. This alliance could strengthen Saudi Arabia’s economic and geopolitical standing, especially in regions where it shares mutual interests with current BRICS members. - Argentina:
Argentina, supported by China, seeks to reduce its dependence on the U.S. dollar and align with BRICS to stabilize its economy. As a major South American economy, Argentina’s membership could further diversify BRICS’ influence. - Ethiopia:
As one of Africa’s fastest-growing economies, Ethiopia sees BRICS as a strategic opportunity to expand its trade partnerships and reduce its reliance on Western financial institutions. - Algeria:
In July, Algeria submitted its application for BRICS membership, alongside a bid to become a shareholder in the New Development Bank (NDB), BRICS’ financial institution.
These prospective members have diverse motivations, from economic stability to seeking new political alliances, but they all view BRICS as a pathway to reduce reliance on Western institutions, especially the U.S. dollar.
Why Do Countries Want to Join BRICS?
Economic Opportunities and Development
BRICS offers countries access to an economic network that promotes trade and investment without depending solely on Western markets. For emerging economies, membership can provide a foundation for economic growth through shared projects, investment in infrastructure, and potential financial support from the New Development Bank.
Reducing Dollar Dependence
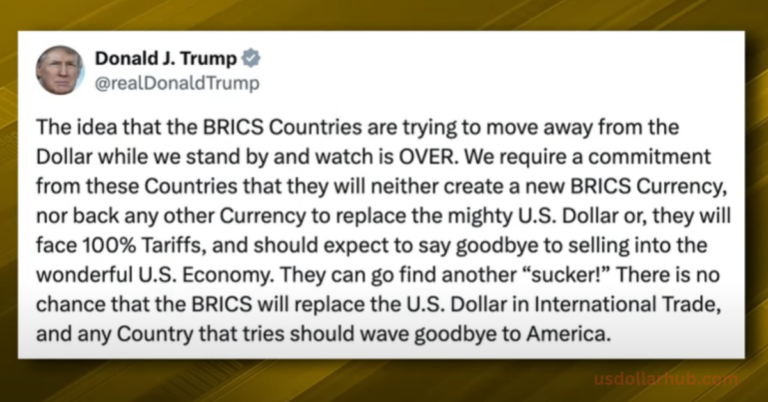
A core appeal of BRICS for many countries is its focus on minimizing dependence on the U.S. dollar in international trade. Bolivia, for instance, recently shifted to using the Chinese yuan in trade, aligning with BRICS’ aim to diversify away from dollar-centric transactions. By reducing reliance on the dollar, these nations can stabilize their own currencies, mitigate inflationary pressures, and foster economic resilience.
Political and Strategic Alliances
Joining BRICS can also allow countries to strengthen their geopolitical positioning. For countries like Iran and Russia, BRICS membership serves as a means to counter Western sanctions and diplomatic isolation. Additionally, BRICS offers a platform for its members to promote their own regional interests, which may not align with Western policies.
Internal Views on Expansion Within BRICS
Despite the interest from multiple nations, current BRICS members hold varied opinions on expanding the group:
- China:
China is a strong proponent of expansion. Its motivations are both economic and strategic, seeking to increase its global influence and counterbalance U.S. dominance, especially in Asia and Africa. - Russia:
Russia also supports BRICS expansion, particularly as it seeks allies amidst its diplomatic isolation following the Ukraine conflict. - South Africa:
South Africa, the group’s current chair, aligns with China and Russia in favoring expansion, viewing it as an opportunity to elevate Africa’s role in global affairs. - Brazil:
Brazil has shown skepticism toward rapid expansion. Concerns center on potential dilution of the group’s effectiveness and cohesion, especially if member interests diverge. - India:
India remains undecided, balancing its membership in BRICS with its strategic relationships with Western nations, particularly the United States.
Potential Impacts of BRICS Expansion
Economic Shifts
As BRICS expands, its influence in the global economy could grow substantially. The addition of new members would bring fresh capital, resources, and markets into the alliance. A larger BRICS coalition could potentially influence global commodity markets, international finance, and trade patterns.
Increased Currency Diversity
If more nations join BRICS, the move away from the U.S. dollar could accelerate. A diversified currency base within BRICS would reduce the dominance of any single currency in global trade, potentially making the international monetary system more stable and resilient.
Geopolitical Rebalancing
A larger BRICS could lead to a more multipolar world order, where multiple regional powers share influence. This shift could challenge the unipolar dominance that the U.S. has enjoyed since the end of the Cold War. Emerging powers in Asia, Africa, and Latin America could see their global influence expand through a stronger BRICS coalition.
Challenges Facing BRICS
Despite its growing appeal, BRICS faces significant challenges, especially regarding expansion:
- Internal Disagreements:
Diverging views on expansion indicate potential friction. Larger membership could complicate consensus-building, especially if new members have conflicting priorities. - Financial and Political Constraints:
Not all prospective members can contribute equally to the group’s goals. Financially weaker nations may struggle to participate meaningfully, adding strain to BRICS’ New Development Bank and other resources. - Western Resistance:
The growth of BRICS could draw pushback from Western nations, particularly the U.S. Potential responses could include economic sanctions, restrictions, or diplomatic pressure on BRICS members and affiliates.
Conclusion
The BRICS coalition represents a powerful economic and political bloc that continues to evolve. As more countries express interest in joining, BRICS has the potential to reshape the global landscape, offering a fresh alternative to Western-dominated institutions and the dollar-based economy. However, the path forward will require careful navigation to ensure cohesion among diverse nations with varying goals. For the U.S. and its allies, BRICS’ expansion underscores the growing influence of emerging economies and the shifting dynamics of global power.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial or investment advice. The views expressed are based on current developments and public reports on BRICS membership and expansion. Readers should consult a financial professional before making any investment decisions.
for More visit Here- Click