BRICS : BRICS Pay, New Members, and the Implications for the U.S. Dollar
BRICS Summit
In recent years, the BRICS alliance — Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa — has steadily grown in influence, posing potential challenges to the U.S.-led global economic order. The 2024 BRICS Summit, held in Kazan, Russia, marked a significant milestone for the alliance, introducing the “BRICS Pay” system and formalizing new member invitations. The developments from this summit have substantial implications for the global economy, particularly the dominance of the U.S. dollar.

This blog will explore the key outcomes of the BRICS Summit, including the introduction of BRICS Pay, the expanding membership, and how this alliance’s strategic actions could reshape the financial landscape for the U.S. dollar and the world at large.
What Is BRICS, and Why Does It Matter?
BRICS
BRICS is a coalition of some of the world’s largest emerging economies — Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. Since its founding in 2009, the group has expanded its initiatives, aiming to support developing economies and provide an alternative to traditional Western-led institutions, such as the IMF. The alliance’s New Development Bank (NDB), established to provide low-conditional loans to member and allied nations, is a direct response to the IMF’s stricter terms.
Why It’s Significant ?
The BRICS countries collectively represent about 42% of the world’s population and 27% of global GDP. With an agenda that promotes alternatives to Western financial structures, BRICS is positioned to challenge the influence of the U.S. dollar, particularly in regions with growing economies and in countries under U.S. sanctions.
2024 BRICS Summit
1. BRICS Pay: An Alternative Payment System
At the Kazan summit, BRICS announced the rollout of BRICS Pay, a payment system that rivals SWIFT, the widely used U.S.-controlled global financial messaging network. BRICS Pay is designed to support transactions among BRICS countries and their allies without relying on the U.S. dollar.
- BRICS Pay Components: The system features a QR code app for retail users, a B2B solution for businesses, a digital currency for internal use, and cross-border settlement services. Currently, only the QR code and B2B functions are operational, with additional features expected in future phases.
- Technology: BRICS Pay is blockchain-based, drawing on Ethereum technology for decentralized, secure transactions. A consortium of financial institutions, primarily banks from BRICS countries, operates the network. The confidentiality surrounding member institutions hints that even some Western banks may be involved.
This payment system provides countries looking to reduce dependence on the U.S. dollar with a functional alternative.
2. Expanding BRICS Membership
The summit also saw the formal invitation of four new members: Ethiopia, Iran, Egypt, and the United Arab Emirates, effective January 1, 2024. Thirteen additional countries, including Saudi Arabia, Turkey, and Nigeria, have expressed interest in joining BRICS, signaling the bloc’s growing appeal.
- New Member Contributions: Countries like the UAE bring wealth and energy resources, while Ethiopia and Egypt offer strategic influence in Africa. This diversification of BRICS’ membership strengthens its economic and geopolitical reach.
- Global Population Impact: With nearly half of the world’s population now represented in BRICS or aligned with its goals, the bloc’s influence has grown significantly. In contrast, the G7 represents only about 10% of the global population.
Implications for the U.S. Dollar
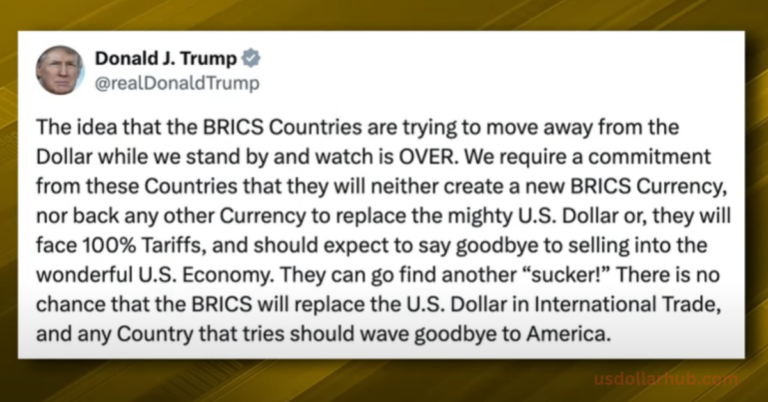
The growing influence of BRICS and its members’ commitment to alternative financial systems pose real challenges for the dominance of the U.S. dollar. Here’s a closer look at why BRICS’ strategies are likely to affect the dollar’s position in global trade and finance.
1. De-dollarization Efforts
The New Development Bank (NDB) has begun issuing loans in non-U.S. dollar currencies, aiming to ease the repayment burden for emerging economies that lack the dollar reserves to manage high-interest debts. This marks a shift toward de-dollarization, which could reduce the demand for U.S. dollars over time.
- Interest Rates and Dollar Debt: Many developing countries are burdened by U.S. dollar-denominated debts, which become harder to pay as the Federal Reserve raises interest rates. For instance, Egypt’s debt to the IMF, primarily in dollars, complicates its financial stability. The NDB’s local-currency loans could alleviate some of this strain.
- Global Influence: By supporting loans in local currencies, BRICS strengthens ties with developing nations. This could lead to a shift away from the dollar as the primary international currency, particularly if more countries join BRICS and adopt similar policies.
2. Rising Demand for Commodities over Currency
A unique characteristic of BRICS nations is their substantial commodity production, including oil, metals, and agricultural goods. Countries may eventually prefer to trade commodities directly or via BRICS Pay rather than relying on dollars.
- Commodity-Based Economy: As the alliance matures, BRICS could establish a commodity-based economy that would allow for direct trade without U.S. dollars. This strategy could bolster the economies of BRICS members while diminishing the dollar’s role in global commodity markets.
- Middle-Class Growth in BRICS Countries: Rising middle-class populations in BRICS nations may increase commodity demand, which in turn, could fuel internal growth without the need for dollar-based trade. If commodity prices continue to rise, the dependency on the dollar will weaken further.
Future of BRICS as a Formal Organization
The Kazan summit highlighted the potential for BRICS to transition into a formal organization, akin to the European Union. Saudi Arabia, one of the interested nations, advocates for an official structure, which would enable BRICS to operate with greater unity. However, Russian President Vladimir Putin expressed hesitations, citing the need to maintain flexibility and avoid bureaucratic delays.
A formal organization could strengthen BRICS’ ability to operate effectively in global finance. This step may depend on whether key members can balance the trade-offs between efficiency and the organizational structures needed for broader influence.
The U.S. Response and Geopolitical Tensions
The U.S. and its allies have exerted pressure on BRICS countries, particularly India, for its ties with Russia and other BRICS members. However, India’s recent decision to deepen relations with BRICS allies and Iran signals a shift. This year, the U.S. imposed sanctions on India due to its economic dealings with Russia, yet India remains resolute in its commitment to BRICS.
As BRICS continues to expand and strengthen, the U.S. faces the challenge of addressing these changing alliances. The Kazan Declaration, which calls for cooperation on BRICS Pay and further non-dollar transactions, indicates that BRICS members are determined to pursue their goals despite external pressure.
Will BRICS Dethrone the Dollar?
The path for BRICS to replace the U.S. dollar as the world’s reserve currency remains complex and long. Major hurdles include:
- Existing Dollar Debts: Countries like Egypt are heavily indebted to Western institutions in U.S. dollars, limiting their ability to fully embrace de-dollarization.
- Economic Stability: Some BRICS nations face economic challenges that could hinder a seamless transition.
- Global Trust and Credibility: The U.S. dollar benefits from trust and stability, which will take time for BRICS to replicate.
What the Future Holds
The BRICS Summit in Kazan brought several ambitious plans to light. While the transition away from the dollar will be gradual, the momentum is undeniable. For the U.S., the rise of BRICS presents both a challenge and an opportunity to re-evaluate its approach to global economics.
Conclusion
The 2024 BRICS Summit is a testament to the growing desire among developing nations to establish a multipolar world economy, independent of U.S. dollar dominance. From the launch of BRICS Pay to the addition of new members, the summit signifies the bloc’s commitment to creating a more balanced global financial landscape.
Disclaimer
This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. Always consult with a qualified professional before making financial decisions related to global currency markets or investments.
Also visit for more updates – click here






One Comment